In this post, I will describe how to install Nacos on the Kubernetes environment. This post requires you to have some basic Kubernetes knowledge and is not suitable for every beginner.
What is Nacos
Nacos is an open-source software provided by Alibaba, which can help you discover, configure and manage your microservices. it supports two major use cases, service registry and config service. Microservice can automatically and dynamically register in Nacos and get application configuration. for detailed information, you can check out from Nacos Official website
To use Nacos, I would recommend deploying Nacos on the Kubernetes cluster environment. This will keep Nacos high availability. you can find the official deployment document, in their demo, they are using NFS as persistent storage.
I will install 3-Pod Nacos Cluster on a single node of Kubernetes and use local PV as persistent storage in this post. it sounds wired indeed, but this was one of our project’s architecture.
Create Database and import SQL file.
You need to create the Nacos database and import an SQL file. there are many ways to do this. the simplest is using MySQL utilities. you can find the Nacos SQL file from GitHub
Create local folder
Create a local folder on the host as a persistent volume destination.
mkdir -p /data/gosysops/localpath-db/nacos/pv1
mkdir -p /data/gosysops/localpath-db/nacos/pv2
mkdir -p /data/gosysops/localpath-db/nacos/pv3
Create Storage Class
To create local volume, a StorageClass is needed. This kind of StorageClass doesn’t support dynamic provisioning. `WaitForFirstConsumer` is to delay volume binding until Pod scheduling.
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: nacos-localpath-storage
provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
Note: Please ensure your Kubernetes has permission to access the host. The Kubernetes created by the RKE tool, you need to add the following into your `Cluster.yaml`
kubelet:
extra_binds:
- "/data:/data"
Create PV
Create 3 Nacos PersistentVoume, – `nacos-local-pv1, nacos-local-pv1, nacos-local-pv3` ,change their name, path in the file respectively.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: nacos-local-pv1
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeMode: Filesystem
storageClassName: nacos-localpath-storage
local:
path: /data/gosysops/localpath-db/nacos/pv1
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- master01
Create Nacos deployment
This Yaml consists of three sections, Service, ConfigMap and Statefulset.
For Nacos Service, you will be able to define and update related ports.
ConfigMap: you can define database username, password, etc. in the yaml, I had added an extra field `mysql.host: mysql-0.mysql-ha`
Statefulset: there are 2 containers in the StatefulSet file, one is the init container, which is used to seek nacos other peers. the second pod is the nacos server. the affinity is commented out because Nacos is deployed on a single node. in the end, we assign a StorageClassName bound to the pod.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nacos-headless
namespace: gosysops-prod
labels:
app: nacos
annotations:
service.alpha.kubernetes.io/tolerate-unready-endpoints: "true"
spec:
ports:
- port: 8848
name: server
targetPort: 8848
- port: 9848
name: client-rpc
targetPort: 9848
- port: 9849
name: raft-rpc
targetPort: 9849
## 兼容1.4.x版本的选举端口
- port: 7848
name: old-raft-rpc
targetPort: 7848
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nacos
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nacos-cm
namespace: gosysops-prod
data:
mysql.host: "mysql-0.mysql-ha"
mysql.db.name: "nacos"
mysql.port: "3306"
mysql.user: "nacos"
mysql.password: "nacos"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: nacos
namespace: gosysops-prod
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nacos
serviceName: nacos-headless
replicas: 3
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nacos
annotations:
pod.alpha.kubernetes.io/initialized: "true"
spec:
#affinity:
# podAntiAffinity:
# requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
# - labelSelector:
# matchExpressions:
# - key: "app"
# operator: In
# values:
# - nacos
# topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
initContainers:
- name: peer-finder-plugin-install
image: nacos/nacos-peer-finder-plugin:1.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /home/nacos/plugins/peer-finder
name: data
subPath: peer-finder
containers:
- name: nacos
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: nacos/nacos-server:1.4.2
resources:
requests:
memory: "3Gi"
cpu: "500m"
ports:
- containerPort: 8848
name: client-port
- containerPort: 9848
name: client-rpc
- containerPort: 9849
name: raft-rpc
- containerPort: 7848
name: old-raft-rpc
env:
- name: NACOS_REPLICAS
value: "3"
- name: SERVICE_NAME
value: "nacos-headless"
- name: DOMAIN_NAME
value: "cluster.local"
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_HOST
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.host
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_DB_NAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.db.name
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_PORT
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.port
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_USER
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.user
- name: MYSQL_SERVICE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: nacos-cm
key: mysql.password
- name: NACOS_SERVER_PORT
value: "8848"
- name: NACOS_APPLICATION_PORT
value: "8848"
- name: PREFER_HOST_MODE
value: "hostname"
volumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /home/nacos/plugins/peer-finder
subPath: peer-finder
- name: data
mountPath: /home/nacos/data
subPath: data
- name: data
mountPath: /home/nacos/logs
subPath: logs
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: data
spec:
storageClassName: "nacos-localpath-storage"
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteMany" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
Deploy Nacos
After saving and applying the above files, you are able to see 3 nacos pods in Kubernetes by kubectl get pod
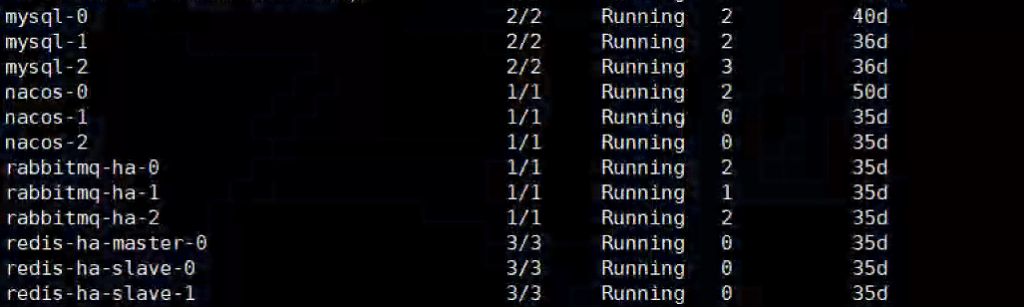
Access Nacos
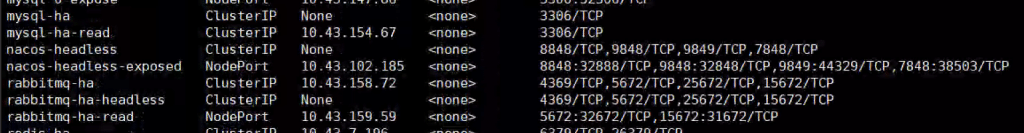
Two ways to access Nacos, Ingress and NodePort. In my internal environment, I created a new service called Nacos-headless-exposed and exposed port 32888 to access.
the default username and password is nacos
Summary
You have learned how to deploy the Nacos cluster on a single Kubernetes node and how to create local volume as persistent storage. I do not usually recommend using it this way. if the node fails, the Nacos cluster is meaningless.